Suicide Prevention for Older Adults: A Critical Need
Suicide prevention for older adults is a critical issue that demands our immediate attention. Alarmingly, this demographic, particularly those aged 75 and older, faces the highest rates of suicide compared to any other age group, yet they have the fewest resources available to them. Research indicates that the mental health of older adults is often overlooked, leading to a dire need for targeted suicide prevention efforts. With increasing use of the internet among seniors, it is essential to enhance the visibility of mental health resources specifically tailored to their unique challenges. By fostering senior suicide awareness and addressing the stigma surrounding geriatric mental health, we can work towards significantly reducing these troubling suicide statistics among the elderly population.
When we discuss the mental well-being of seniors, it’s crucial to highlight the pressing need for effective suicide prevention initiatives aimed specifically at this age group. Older individuals face unique challenges that can severely impact their mental health, including isolation and loss, contributing to a troubling rise in suicide rates. As we explore the landscape of older adults’ mental health, we must broaden our focus on geriatric suicide prevention, ensuring that resources and support systems are readily accessible. The growing concern for senior mental wellness requires increased awareness and advocacy to help decrease the alarming statistics surrounding the elderly. By providing comprehensive mental health resources for seniors, we can empower them to seek the help they need in a supportive environment.
Understanding the Crisis: Suicide Statistics Among Older Adults
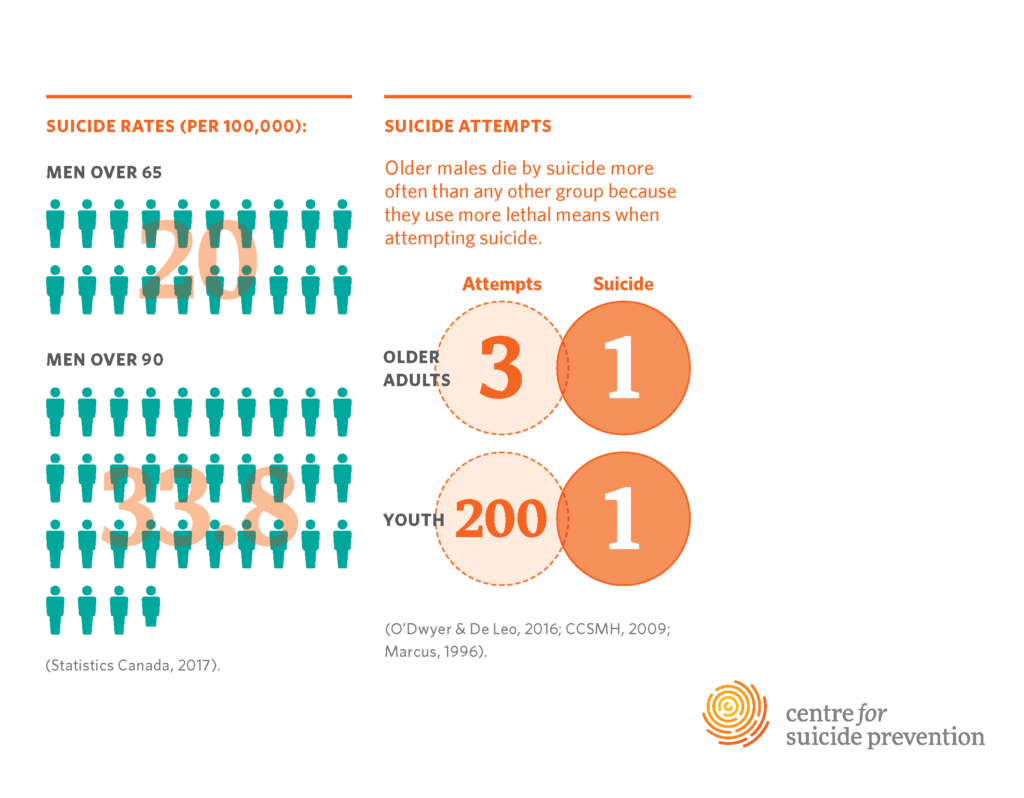
Older adults, particularly those aged 75 and older, face a disturbing reality when it comes to mental health and suicide risk. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), adults in this age cohort have one of the highest suicide rates, estimated at 20.3 per 100,000. This concerning statistic places older adults at the forefront of an urgent public health crisis that demands immediate attention and action. The increasing rates of suicide among seniors are starkly contrasted against decreasing rates in younger populations, highlighting a growing issue in geriatric mental health that warrants a focused response from both healthcare providers and policymakers.
Several factors contribute to this alarming trend in suicide rates among older adults. Social isolation, loneliness, and the challenges associated with aging—such as loss of loved ones and declining health—are significant risks that often go unaddressed. Moreover, there is an evident gap in mental health resources for seniors, as most public health initiatives and campaigns primarily target younger demographics. Understanding the unique circumstances of older adults and the barriers they face in accessing mental health care is crucial for developing effective suicide prevention strategies tailored specifically for this vulnerable group.
The Need for Targeted Suicide Prevention for Older Adults
Addressing suicide prevention for older adults necessitates a comprehensive approach that considers the distinct healthcare needs of seniors. Despite their high risk, many national suicide prevention organizations have not adequately created or disseminated resources that resonate with this audience. This disparity highlights an urgent need for targeted campaigns designed to reach older adults. Awareness and accessibility are paramount; hence, efforts must be redirected to ensure that older adults can easily find and relate to the mental health resources available to them.
Research indicates that public-facing suicide prevention campaigns can be quite effective; however, the existing initiatives often overlook the aging population. It is critical for stakeholders, including healthcare organizations, to invest in creating tailored messaging that addresses the particular concerns of older adults grappling with mental health challenges. Empowering seniors with knowledge and access to support systems can significantly reduce the stigma surrounding mental health issues, fostering an environment where they feel comfortable seeking help.
Enhancing Mental Health Resources for Seniors
To combat the rising rates of suicide among older adults, there is a pressing need to enhance mental health resources specifically designed for seniors. Current research has revealed a numerical imbalance in the availability of these resources, with many platforms focusing their efforts on younger age groups instead. With older adults increasingly turning to the internet for health information, it is essential that mental health resources are not only present but are also user-friendly and accessible. This requires collaboration among healthcare providers, tech developers, and community organizations to create platforms that cater to the needs of older users.
Additionally, increasing funding for geriatric mental health programs is imperative. By investing in outreach campaigns that inform older adults about available resources, communities can foster better awareness and ultimately encourage more seniors to seek the support they need. Creating engaging content that speaks directly to older adults’ experiences, including clear pathways to mental health services, is vital to effectively address their unique challenges regarding mental health.
The Role of Social Connectivity in Preventing Senior Suicide
Social connectivity plays a crucial role in mitigating suicide risk among older adults. Loneliness and social isolation are significant contributors to mental health challenges in this population, leading to feelings of despair and decreased overall well-being. By fostering community connections, older adults can engage in meaningful relationships and activities that promote mental health. Organizations can help by facilitating social programs that bring seniors together, thereby creating a sense of belonging and support that is vital for their emotional health.
Moreover, initiatives that incorporate family engagement and support systems into preventive measures can be incredibly beneficial. Educating family members about the signs of mental health distress and equipping them with the tools to support their elderly relatives can help create a protective buffer against feelings of loneliness and hopelessness. An integrated approach that takes into account the social aspects of aging will be essential for effective suicide prevention for older adults.
Barriers to Seeking Help: Understanding Older Adults’ Mental Health Needs
Older adults often face unique barriers when it comes to seeking help for mental health issues, including stigma, lack of awareness, and limited access to resources. Many seniors may feel reluctant to discuss their mental health needs due to fear of judgment or not being understood. These barriers can prevent them from reaching out for assistance, exacerbating feelings of isolation and despair. To combat this, it’s crucial to create a supportive environment that encourages older adults to talk about their mental health concerns openly.
Additionally, practical barriers such as transportation issues, physical disabilities, and inadequate insurance coverage can hinder access to mental health services. It is essential for mental health practitioners and organizations to recognize these obstacles and work towards eliminating them. This could mean offering virtual consultations tailored for older adults, providing transportation assistance, or improving healthcare coverage for mental health services. By addressing these barriers, we can better support older adults in their journey towards improved mental health.
The Importance of Awareness in Senior Suicide Prevention
Awareness is a crucial component of suicide prevention among older adults. Raising public consciousness about the specific mental health needs of seniors can lead to more informed communities that are better equipped to provide support. Awareness campaigns can help demystify mental health issues, reduce stigma, and encourage open discussions within families and communities surrounding suicide risks in older populations. By fostering an environment of understanding, older adults may feel more comfortable seeking the help they need.
Additionally, educational programs targeting healthcare providers are equally important. Training those who work with older adults to recognize the signs of mental distress can lead to early intervention and support. A well-informed healthcare workforce can make a significant difference in identifying at-risk seniors and facilitating access to the mental health resources they need. By embedding awareness into the fabric of community health initiatives, we can create a robust safety net for older adults that ultimately reduces suicide rates.
Community Engagement as a Strategy for Supporting Senior Mental Health
Community engagement is a powerful strategy for enhancing mental health support for older adults. By creating initiatives that encourage seniors to participate in community life, we can help reduce isolation and promote emotional well-being. Community centers, libraries, and local organizations can serve as hubs for social activities, workshops, and support groups tailored specifically for seniors. Such programming not only provides entertainment and education but also fosters meaningful interactions that can improve mental health outcomes.
Moreover, involving older adults in the planning and execution of these community activities ensures that their voices and preferences are considered, leading to more relevant and engaging programs. This participatory approach can enhance feelings of purpose and value among seniors, which are vital components in preventing mental health crises. By building strong community ties and supporting social networks, we can create a foundation for healthier aging that directly addresses the risks associated with suicide in older adults.
The Essential Role of Family Support in Mental Health for Seniors
Family support plays an indispensable role in the mental health of older adults. Close connections with family members can provide emotional support, companionship, and a sense of belonging, all of which are critical for preventing feelings of isolation that contribute to increased suicide risk. Encouraging family discussions around mental health can help reduce stigma and promote open communication, allowing seniors to express their challenges and seek the support they need.
Furthermore, educating families about the mental health resources available can empower them to assist their loved ones in accessing necessary support services. By fostering a culture of caregiving and empathy within families, we can create an environment where older adults feel safe and valued, ultimately reducing the likelihood of mental health crises. Supportive family networks can act as a buffer against the emotional toll of aging, helping seniors navigate their mental health challenges more effectively.
Future Directions: Research and Funding for Senior Mental Health Initiatives
As the population of older adults continues to grow, there is an urgent need for increased research and funding dedicated to mental health initiatives targeting this demographic. Current studies show a lack of resources specifically aimed at addressing the unique mental health challenges faced by seniors, which indicates a significant gap in our healthcare system. Future research should focus on identifying the most effective prevention strategies, treatments, and outreach programs that resonate with older adults.
In addition, funding for geriatric mental health services must be prioritized to develop community-based programs that address the specific needs of older adults. This includes ensuring that mental health resources are accessible, culturally sensitive, and effective in promoting wellness among seniors. By investing in this critical area, we can move towards a more comprehensive approach to healthcare that acknowledges and addresses the complex mental health landscape facing older adults.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key suicide prevention strategies for older adults?
Suicide prevention for older adults focuses on enhancing mental health resources for seniors, addressing issues like social isolation, and providing targeted intervention programs. Strategies may include promoting awareness of senior suicide statistics, encouraging social engagement, and facilitating access to geriatric mental health services.
How significant is the issue of suicide among older adults?
Suicide rates among older adults, particularly those aged 75 and older, are alarmingly high. According to the CDC, this age group experiences a rate of 20.3 per 100,000, highlighting the need for focused suicide prevention efforts and greater awareness of older adults’ mental health.
Where can older adults find mental health resources for suicide prevention?
Despite the high risk of suicide among older adults, mental health resources for seniors are often not prominently featured on major health websites. It’s essential for seniors to seek out tailored resources, such as local geriatric mental health services, community support groups, and helplines specifically aimed at addressing senior suicide awareness.
What role does social isolation play in senior suicide rates?
Social isolation significantly contributes to increased suicide statistics in the elderly population. Older adults may experience loneliness, leading to an elevated risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors. Addressing this issue is critical in suicide prevention for older adults, by fostering community connections and social networks.
How can communities improve suicide prevention efforts for older adults?
Communities can enhance suicide prevention efforts for older adults by developing targeted awareness campaigns, increasing funding for mental health programs, and ensuring easy access to geriatric mental health resources. Programs should focus on reducing stigma, encouraging open discussions about mental health, and providing practical support for seniors.
What specific challenges do older adults face when seeking help for mental health issues?
Older adults often face unique challenges when seeking mental health help, including systemic biases, lack of tailored information, and limited access to services. These barriers underscore the necessity for improved suicide prevention for older adults, ensuring resources meet the specialized needs of this demographic.
Why is there a need for awareness campaigns focusing on senior suicide prevention?
Awareness campaigns focusing on senior suicide prevention are crucial because they can help address the disparities in resources available to older adults. Such campaigns raise awareness about the unique challenges this population faces and promote the available mental health resources, ultimately aiming to reduce the rising suicide rates among elderly individuals.
How can family members support older adults at risk of suicide?
Family members can play a vital role in suicide prevention for older adults by fostering open communication about mental health, recognizing signs of distress, and encouraging them to seek help. Providing emotional support, promoting social interaction, and helping access appropriate mental health resources are essential ways families can support their elderly relatives.
What is the impact of implicit biases on older adults’ mental health treatment?
Implicit biases can hinder effective mental health treatment for older adults, leading to underrepresentation in research and a lack of tailored interventions. Recognizing these biases is crucial to develop better suicide prevention strategies and improved mental health resources for seniors.
Are there online resources specifically designed for older adults experiencing suicidal thoughts?
While there are online resources for mental health, many are not specifically tailored for older adults. Therefore, it is important for older individuals to seek out platforms that focus on senior suicide awareness, which may include dedicated helplines, websites, and community organizations that understand and address their unique needs.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| High Risk of Suicide | Older adults, particularly those aged 75 and older, have the highest suicide rates among age groups. |
| Imbalance in Resources | Study reveals that national suicide prevention organizations do not provide easily accessible resources for older adults. |
| Online Resource Scarcity | Investigators found few resources targeting older adults despite high visibility of suicide risk acknowledged online. |
| Increased Need for Campaigns | Public-facing campaigns effective; urgent need for similar initiatives for older adults. |
| Call for Research and Funding | The study emphasizes the need for tailored prevention programming and increased funding for research. |
Summary
Suicide prevention for older adults is an urgent public health need that cannot be overlooked. The alarming rates of suicide among individuals aged 75 and older indicate a critical gap in available resources and support. This demographic faces unique challenges, including increased feelings of isolation and insufficient representation in existing suicide prevention efforts. As highlighted in recent studies, the disparity in targeting and accessibility of online resources accentuates the necessity for more focused and tailored campaigns aimed at older adults. Moving forward, it is essential for stakeholders and organizations to prioritize the development of accessible and effective suicide prevention strategies that cater specifically to the needs of this vulnerable population.